二维码支付的4种方式:技术原理解析
- 前言
- 问题一:谁出示二维码?
- 1. 消费者出示模式(Consumer-Presented Mode)
- 2. 商家出示模式(Merchant-Presented Mode)
- 问题二:二维码是动态还是静态?
- 1. 动态二维码(Dynamic QR Code)
- 2. 静态二维码(Static QR Code)
- 四种方式的组合与应用
- 1. 消费者出示 + 动态二维码
- 2. 消费者出示 + 静态二维码
- 3. 商家出示 + 动态二维码
- 4. 商家出示 + 静态二维码
- 技术实现对比
- 安全性对比
- 性能对比
- 实际案例分析
- 案例1:微信支付的实现
- 案例2:支付宝的实现
- 未来发展趋势
- 1. 技术演进方向
- 2. 安全性提升
- 总结与建议
- 选择指南
- 技术选型建议
- 安全最佳实践
作者:技术解析
难度等级:中级
预计阅读时间:10分钟
字数:约1500字
前言
每天,全球有数十亿次交易通过二维码完成。从街边小店到跨国超市,从公交地铁到在线购物,二维码支付已经成为我们生活中不可或缺的一部分。
但你是否知道,看似简单的"扫一扫"背后,其实隐藏着4种完全不同的技术实现方式?这些方式在安全性、用户体验和适用场景上有着显著差异。
今天,我们将通过两个核心问题来深入剖析二维码支付的技术内幕:
1. 谁出示二维码? - 消费者还是商家?
2. 二维码是动态还是静态? - 实时生成还是一次性固定?
通过这篇文章,你将彻底理解二维码支付的技术原理,并能根据实际需求选择最适合的方案。
问题一:谁出示二维码?
二维码支付的第一个关键维度是二维码的出示方,这决定了支付流程的发起者和控制权。
1. 消费者出示模式(Consumer-Presented Mode)
在这种模式下,消费者出示二维码,商家使用扫描设备进行扫描。
支付流程:
消费者打开支付App → 生成付款码 → 商家扫描 → 实时扣款 → 支付完成
真实场景:
- 超市收银台:你出示微信/支付宝付款码
- 公交地铁:出示乘车码
- 便利店:出示会员码
技术实现原理:
// 消费者端:生成支付二维码
class ConsumerQRGenerator {
constructor(userId, amount, currency) {
this.userId = userId;
this.amount = amount;
this.currency = currency;
this.timestamp = Date.now();
this.nonce = this.generateNonce();
}
generateQRData() {
return {
type: "consumer_presented",
userId: this.userId,
amount: this.amount,
currency: this.currency,
timestamp: this.timestamp,
nonce: this.nonce,
signature: this.generateSignature()
};
}
generateSignature() {
// 使用私钥对数据进行签名,确保不可篡改
const data = `${this.userId}${this.amount}${this.timestamp}${this.nonce}`;
return this.signWithPrivateKey(data);
}
}
商家扫描端处理:
class MerchantScanner {
async scanAndProcess(qrData) {
// 1. 验证二维码签名(防篡改)
const isValid = await this.verifySignature(qrData);
if (!isValid) {
throw new Error("二维码签名验证失败");
}
// 2. 检查二维码时效性(通常有效期为1-5分钟)
if (Date.now() - qrData.timestamp > 300000) {
throw new Error("二维码已过期");
}
// 3. 发起扣款请求
const paymentResult = await this.requestPayment({
userId: qrData.userId,
amount: qrData.amount,
currency: qrData.currency,
merchantId: this.merchantId
});
return paymentResult;
}
}
技术特点分析:
| 特性 | 说明 | 技术实现 |
|---|---|---|
| 实时性 | 二维码通常有1-5分钟有效期 | 时间戳 + 过期检查 |
| 网络依赖 | 商家设备必须实时联网 | WebSocket/HTTP长连接 |
| 安全性 | 通过签名机制防止篡改 | 非对称加密 + 数字签名 |
| 用户体验 | 支付速度快(1-2秒) | 优化扫描和验证流程 |
优势:
- ✅ 支付速度快,适合高频小额交易
- ✅ 安全性高,动态生成防复制
- ✅ 用户体验流畅,无需输入金额
挑战:
- ❌ 需要实时联网,离线场景受限
- ❌ 对商家设备有一定要求
- ❌ 二维码过期需要重新生成
2. 商家出示模式(Merchant-Presented Mode)
在这种模式下,商家出示二维码,消费者使用手机扫描进行支付。
支付流程:
商家生成收款码 → 消费者扫描 → 确认支付信息 → 授权扣款 → 支付完成
真实场景:
- 餐厅桌台码:扫码点餐支付
- 零售店铺:固定收款码
- 线上线下融合:线上下单,线下扫码支付
技术实现原理:
// 商家端:生成收款二维码
class MerchantQRGenerator {
constructor(merchantId, amount, orderId) {
this.merchantId = merchantId;
this.amount = amount;
this.orderId = orderId;
this.timestamp = Date.now();
this.qrType = "merchant_presented";
}
generateQRData() {
return {
type: this.qrType,
merchantId: this.merchantId,
amount: this.amount,
orderId: this.orderId,
timestamp: this.timestamp,
// 静态二维码可能不包含金额
isDynamic: this.amount !== null
};
}
}
// 消费者端:扫描并处理
class ConsumerScanner {
async scanAndPay(qrData) {
// 1. 解析二维码数据
const { merchantId, amount, orderId } = qrData;
// 2. 显示支付确认界面(关键安全步骤)
const confirmed = await this.showPaymentConfirm({
merchantId,
amount,
orderId
});
if (!confirmed) {
throw new Error("用户取消支付");
}
// 3. 用户授权,发起支付
const paymentResult = await this.authorizePayment({
merchantId,
amount,
orderId,
consumerId: this.consumerId
});
return paymentResult;
}
}
技术特点分析:
| 特性 | 说明 | 技术实现 |
|---|---|---|
| 用户体验 | 消费者有充分确认时间 | 支付确认界面 |
| 离线支持 | 静态二维码可离线展示 | 本地生成和存储 |
| 授权机制 | 需要消费者明确授权 | 用户交互确认 |
| 灵活性 | 支持复杂业务逻辑 | 订单关联、优惠计算 |
优势:
- ✅ 用户体验友好,有确认环节
- ✅ 支持离线场景(静态码)
- ✅ 可关联复杂订单信息
挑战:
- ❌ 支付速度相对较慢
- ❌ 需要消费者主动操作
- ❌ 对网络有一定依赖
问题二:二维码是动态还是静态?
二维码支付的第二个关键维度是二维码的动态性,这直接影响了二维码的安全性和使用便利性。
1. 动态二维码(Dynamic QR Code)
动态二维码是在每次展示时实时生成的,通常包含丰富的交易信息。
技术实现:
class DynamicQRCode {
constructor(transactionData) {
this.data = transactionData;
this.expiryTime = 300000; // 5分钟有效期
this.generationTime = Date.now();
}
generate() {
// 包含完整的交易信息
const qrContent = {
version: "2.0",
transaction: {
id: this.generateTransactionId(),
type: this.data.type,
amount: this.data.amount,
currency: this.data.currency,
merchant: this.data.merchant,
consumer: this.data.consumer,
timestamp: this.generationTime,
expiry: this.generationTime + this.expiryTime
},
security: {
signature: this.generateSignature(),
nonce: this.generateNonce(),
encryption: this.data.encryption || "AES-256-GCM"
},
metadata: {
app: "payment-system",
version: "1.0",
device: this.data.deviceId
}
};
return this.encodeToQR(qrContent);
}
validate() {
const now = Date.now();
if (now > this.data.expiry) {
return { valid: false, reason: "expired" };
}
// 验证签名
const isValid = this.verifySignature(this.data);
return { valid: isValid, reason: isValid ? "valid" : "invalid_signature" };
}
}
动态二维码的特点:
| 特性 | 说明 | 技术实现 |
|---|---|---|
| 时效性 | 通常1-5分钟有效期 | 时间戳 + 过期检查 |
| 信息丰富 | 包含完整交易详情 | JSON结构化数据 |
| 安全性高 | 每次生成唯一签名 | 非对称加密 + 数字签名 |
| 防重放 | 包含随机数(nonce) | 唯一性验证 |
| 可追踪 | 包含完整交易链 | 事务ID + 时间戳 |
安全机制示例:
// 多层安全验证
class DynamicQRSecurity {
async validateQRCode(qrData) {
const checks = [
this.checkExpiry(qrData),
this.checkSignature(qrData),
this.checkNonce(qrData), // 防重放攻击
this.checkTransactionLimits(qrData),
this.checkBlacklist(qrData)
];
const results = await Promise.all(checks);
return results.every(r => r.passed);
}
checkNonce(qrData) {
// 检查nonce是否已被使用(防重放)
const used = this.nonceCache.has(qrData.security.nonce);
if (!used) {
this.nonceCache.set(qrData.security.nonce, Date.now());
// 设置nonce过期时间(如5分钟)
setTimeout(() => {
this.nonceCache.delete(qrData.security.nonce);
}, 300000);
}
return { passed: !used, reason: used ? "nonce_reused" : "valid" };
}
}
2. 静态二维码(Static QR Code)
静态二维码是一次性生成的,通常不包含交易信息或只包含固定信息。
技术实现:
class StaticQRCode {
constructor(merchantId, fixedData) {
this.merchantId = merchantId;
this.fixedData = fixedData;
this.qrType = "static";
}
generate() {
// 静态二维码通常只包含商户标识
const qrContent = {
version: "1.0",
type: this.qrType,
merchant: {
id: this.merchantId,
name: this.fixedData.merchantName,
category: this.fixedData.category
},
// 不包含具体金额,金额由支付时确定
payment: {
method: "dynamic_amount",
currency: this.fixedData.currency || "CNY"
},
// 可能包含固定费率或折扣信息
rules: this.fixedData.rules || null
};
return this.encodeToQR(qrContent);
}
// 静态二维码的支付处理
processPayment(scanData) {
// 扫描时需要额外输入金额
const amount = scanData.amount;
const consumerId = scanData.consumerId;
return {
merchantId: this.merchantId,
amount: amount,
consumerId: consumerId,
timestamp: Date.now(),
// 静态二维码需要额外验证
requiresVerification: true
};
}
}
静态二维码的特点:
| 特性 | 说明 | 技术实现 |
|---|---|---|
| 持久性 | 永久有效,无需更新 | 一次性生成,长期使用 |
| 信息简单 | 通常只包含商户ID | 最小化数据结构 |
| 离线支持 | 无需联网即可展示 | 本地生成和存储 |
| 灵活性 | 支付金额动态确定 | 支付时输入或协商 |
| 成本低 | 无需频繁更新 | 一次生成,多次使用 |
安全考虑:
class StaticQRSecurity {
constructor() {
this.merchantWhitelist = new Set();
this.rateLimiting = new Map();
}
validateStaticPayment(scanData) {
const { merchantId, consumerId, amount } = scanData;
// 1. 商户白名单验证
if (!this.merchantWhitelist.has(merchantId)) {
return { valid: false, reason: "merchantnotwhitelisted" };
}
// 2. 金额合理性检查
if (amount <= 0 || amount > this.getMaxAmount(consumerId)) {
return { valid: false, reason: "invalid_amount" };
}
// 3. 频率限制(防刷)
const key = `${consumerId}_${merchantId}`;
const now = Date.now();
const recent = this.rateLimiting.get(key) || [];
// 清理过期记录(1小时内)
const filtered = recent.filter(time => now - time < 3600000);
if (filtered.length >= 10) { // 限制1小时内最多10次
return { valid: false, reason: "ratelimitexceeded" };
}
filtered.push(now);
this.rateLimiting.set(key, filtered);
return { valid: true };
}
}
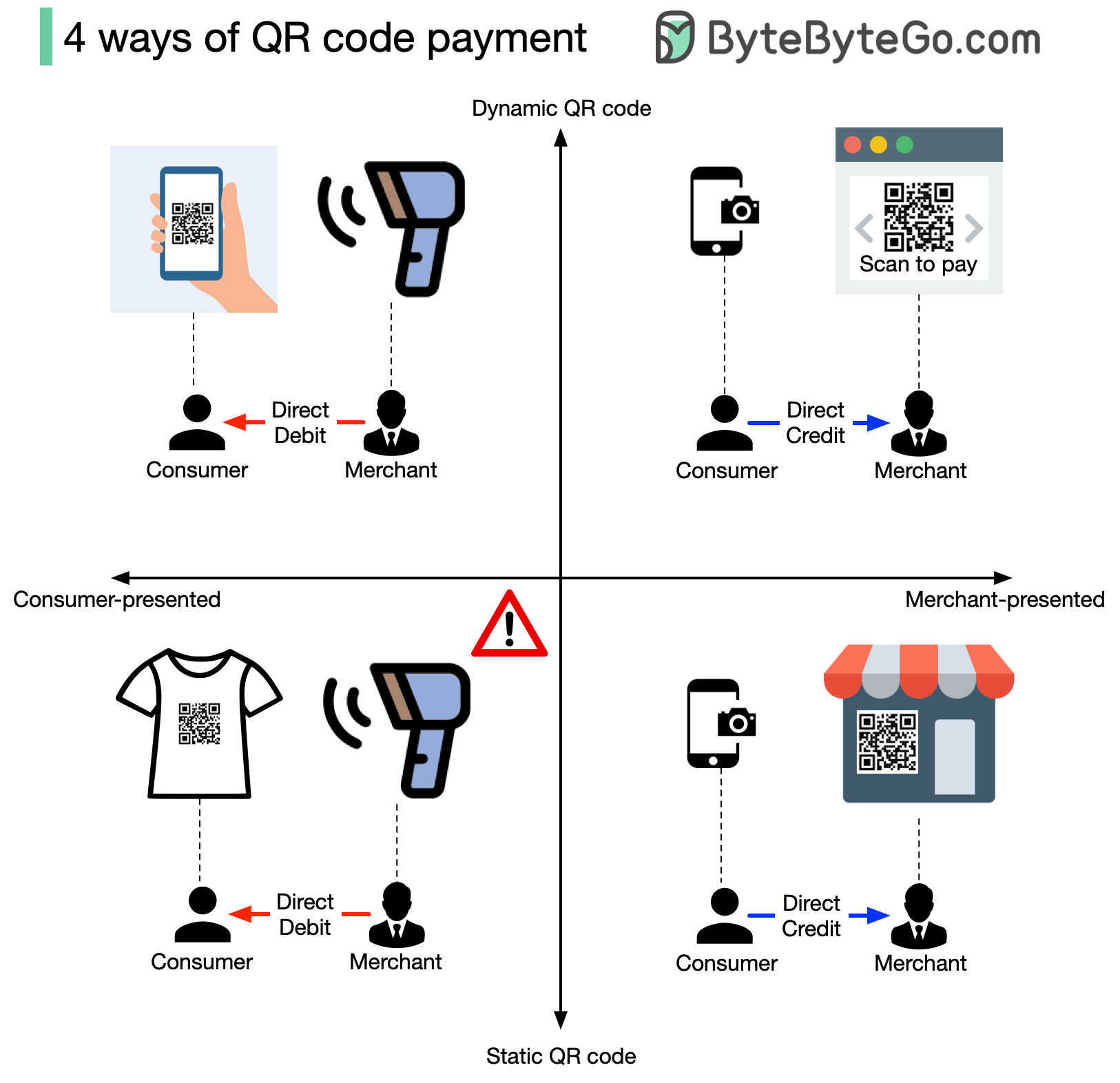
四种方式的组合与应用
通过两个维度的组合,我们得到4种二维码支付方式:
1. 消费者出示 + 动态二维码
典型应用: 超市收银、公共交通
const consumerDynamicQR = {
mode: "consumer_presented",
qrType: "dynamic",
security: "high",
useCase: "快速结账",
example: "微信支付付款码、支付宝付款码"
};
优势:
- 支付速度快(1-2秒)
- 安全性高(动态生成)
- 适合高频小额支付
挑战:
- 需要实时联网
- 对设备性能要求较高
2. 消费者出示 + 静态二维码
典型应用: 会员卡、固定折扣码
const consumerStaticQR = {
mode: "consumer_presented",
qrType: "static",
security: "中等",
useCase: "会员识别、固定优惠",
example: "会员码、固定折扣码"
};
优势:
- 无需联网即可展示
- 适合离线环境
- 便于打印和携带
挑战:
- 安全性相对较低
- 功能相对固定
3. 商家出示 + 动态二维码
典型应用: 餐厅点餐、零售收款
const merchantDynamicQR = {
mode: "merchant_presented",
qrType: "dynamic",
security: "高",
useCase: "精确收款、订单关联",
example: "餐厅桌台码、零售订单码"
};
优势:
- 用户体验好(有确认时间)
- 可关联具体订单
- 支持复杂业务逻辑
挑战:
- 需要消费者主动操作
- 对网络有依赖
4. 商家出示 + 静态二维码
典型应用: 小微商户、固定收款
const merchantStaticQR = {
mode: "merchant_presented",
qrType: "static",
security: "中等",
useCase: "小微商户、固定收款",
example: "个人收款码、固定店铺码"
};
优势:
- 成本低,易于部署
- 无需复杂设备
- 适合小微商户
挑战:
- 金额需要手动输入
- 安全性依赖额外验证
技术实现对比
安全性对比
| 方式 | 身份验证 | 防篡改 | 防重放 | 时效性 | 综合评分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 消费者+动态 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 5.0 |
| 消费者+静态 | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 3.5 |
| 商家+动态 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 4.5 |
| 商家+静态 | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 3.0 |
性能对比
| 方式 | 生成成本 | 扫描速度 | 网络依赖 | 设备要求 | 适用规模 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 消费者+动态 | 中 | 快 | 强 | 中 | 大型商户 |
| 消费者+静态 | 低 | 快 | 弱 | 低 | 个人用户 |
| 商家+动态 | 中 | 中 | 强 | 中 | 中型商户 |
| 商家+静态 | 低 | 慢 | 弱 | 低 | 小微商户 |
实际案例分析
案例1:微信支付的实现
// 微信支付付款码(消费者+动态)
class WeChatPaymentCode {
generate() {
return {
type: "consumer_dynamic",
codeType: "auth_code",
encryptType: "AES-256",
// 每分钟更新一次
refreshInterval: 60000,
// 包含设备信息和用户标识
deviceInfo: this.getDeviceInfo(),
userInfo: this.getUserInfo()
};
}
}
// 微信收款码(商家+静态)
class WeChatMerchantQR {
generate() {
return {
type: "merchant_static",
merchantId: this.merchantId,
fixedAmount: null, // 金额由支付时确定
有效期: "永久",
features: ["固定收款", "支持备注"]
};
}
}
案例2:支付宝的实现
// 支付宝付款码(消费者+动态)
class AlipayPaymentCode {
constructor() {
this.refreshInterval = 60000; // 1分钟刷新
this.encryption = "RSA2";
}
generate() {
return {
code: this.generateAuthCode(),
timestamp: Date.now(),
sign: this.signData(),
// 动态包含交易信息
transaction: {
maxAmount: 5000, // 单笔限额
dailyLimit: 20000 // 日限额
}
};
}
}
// 支付宝收款码(商家+静态)
class AlipayMerchantQR {
generate() {
return {
type: "fixed_qr",
merchant: this.merchantInfo,
payment: {
method: "scan_pay",
currency: "CNY",
// 不包含具体金额
amount: "dynamic"
},
features: ["信用卡支持", "花呗分期"]
};
}
}
未来发展趋势
1. 技术演进方向
// 下一代二维码支付技术
class NextGenQRPayment {
constructor() {
this.technologies = [
"生物识别集成",
"区块链技术",
"AI风控",
"物联网支付",
"跨链支付"
];
}
futureFeatures() {
return {
// 无感支付
frictionless: {
faceRecognition: true,
gestureControl: true,
voiceAuth: true
},
// 智能风控
intelligent: {
realTimeRiskScoring: true,
behaviorAnalysis: true,
fraudDetection: true
},
// 跨平台兼容
interoperability: {
crossBorder: true,
crossCurrency: true,
crossPlatform: true
}
};
}
}
2. 安全性提升
// 增强安全机制
class EnhancedSecurity {
constructor() {
this.methods = [
"量子加密",
"零知识证明",
"多方计算",
"同态加密"
];
}
implementSecurity() {
return {
// 量子安全
quantumSafe: {
algorithm: "Lattice-based",
keySize: 256,
resistance: "quantum_computing"
},
// 隐私保护
privacy: {
zeroKnowledge: true,
dataMinimization: true,
userConsent: true
}
};
}
}
总结与建议
选择指南
根据业务场景选择:
- 大型零售/超市
- 推荐:消费者出示 + 动态二维码
- 理由:速度快、安全性高、适合高频交易
- 餐饮服务
- 推荐:商家出示 + 动态二维码
- 理由:用户体验好、可关联订单、支持复杂场景
- 小微商户/个人
- 推荐:商家出示 + 静态二维码
- 理由:成本低、易于部署、维护简单
- 会员系统/固定优惠
- 推荐:消费者出示 + 静态二维码
- 理由:离线可用、便于携带、功能固定
技术选型建议
// 技术选型决策树
function selectQRPaymentType(requirements) {
const { security, speed, cost, offline, complexity } = requirements;
if (security > 8 && speed > 7) {
return "consumer_dynamic"; // 消费者+动态
} else if (security > 7 && offline) {
return "merchant_dynamic"; // 商家+动态
} else if (cost < 5 && complexity < 5) {
return "merchant_static"; // 商家+静态
} else {
return "consumer_static"; // 消费者+静态
}
}
安全最佳实践
- 动态二维码优先:对于涉及资金的交易,优先使用动态二维码
- 多层验证:结合签名、时效性、频率限制等多重验证
- 实时监控:建立实时风控系统,监控异常交易
- 用户教育:提醒用户保护二维码,避免截屏分享
- 定期更新:及时更新加密算法和安全协议
记住:技术的价值在于解决实际问题。理解这4种方式,你就能更好地设计和选择适合自己业务的支付方案。 🚀

评论
发表评论
|
|
|